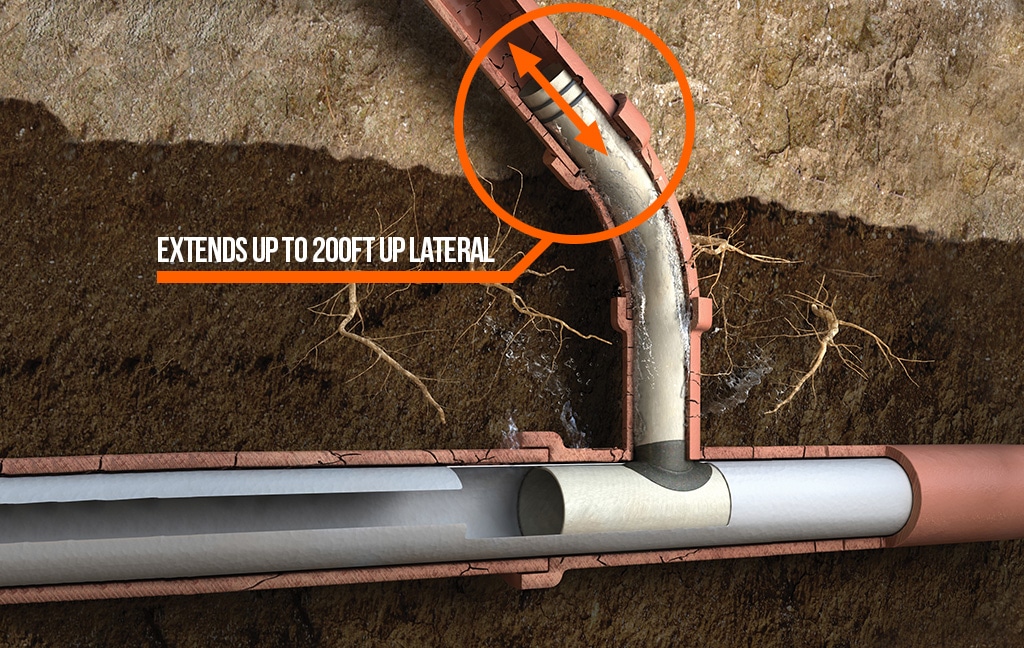
LMK’s T-Liner is an engineered, full-circle structural main-to-lateral connection that also renews lateral pipes in one continuous length up to 200 feet without cold joints. Fully compliant with ASTM standards, this rehabilitation system can be designed and stamped by a licensed P.E. from the installation state for both the lateral and the main-to-lateral structural connection.
ASTM F2561
Standard Practice for Rehabilitation of a Sewer Service Lateral and Its Connection to the Main Using a One Piece Main and Lateral Cured-in-Place Liner
Significance and Use
Purchase the full version of this standard by visiting the ASTM website here. This practice is for use by designers and specifiers, regulatory agencies, owners, and inspection organizations who are involved in the rehabilitation of sewer service laterals and its connection to the main through the use of a resin-impregnated tube installed within an existing sewer lateral. As for any practice, modifications may be required for specific job conditions.
1. SCOPE
- This practice covers requirements and test methods for the reconstruction of a sewer service lateral pipe having an inner diameter of 3 to 12 in. and its connection to the main pipe having an inner diameter of 6 to 24 in. without excavation. The lateral pipe is accessed remotely from the main pipe and from a lateral cleanout. This will be accomplished by the installation of a resin impregnated one-piece main and lateral cured in-place lining (MLCIPL) by means of air or water inflation and inversion. The MLCIPL is pressed against the host pipe by pressurizing a bladder and is held in place until the thermoset resins have cured. When cured, the MLCIPL shall be a continuous, one piece, tight fitting, corrosion resistant lining extending over a predetermined length of the lateral pipe and the adjacent section of the main pipe providing a verifiable non-leaking structural connection and seal.
- The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
- There is no similar or equivalent ISO Standard.
- This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Particular attention is drawn to those safety regulations and requirements involving entering into and working in confined spaces.
2. REFERENCED DOCUMENTS.
- D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
- D3681 Test Method for Chemical Resistance of “Fiberglass” (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin) Pipe in a Deflected Condition
- D5813 Specification for Cured-In-Place Thermosetting Resin Sewer Piping Systems
- D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
- D790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
- F1216 Practice for Rehabilitation of Existing Pipelines and Conduits by the Inversion and Curing of a Resin-Impregnated Tube
- F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
- Recommended Specifications for Sewer Collection System Rehabilitation
INDEX TERMS
ambient cure; continuous; cured in place pipe; epoxy; felt; hydrophilic o-rings; inflation; inversion; knit; lateral identification; lateral pipe; lateral tube; launcher; liner/bladder assembly; main pipe; main sheet; main to lateral connection; MLCIPL; one-piece; resin; sewer lateral lines; sheet; steam cure; TEE; textile sheet; textile tube; transition; translucent bladder; tube; vacuum impregnate; WYE; ICS Number Code 93.030 (External sewerage systems)
DOI
DOI: 10.1520/F2561-17
For a copy of the ASTM F2561 Standard please visit www.astm.org
LMK Technologies has pioneered CIPP lateral renewal technology and has driven the industry forward with new products and technologies to facilitate sewer rehabilitation of sewers for 20 years. In its relatively small lifespan as a company, LMK has invested time and resources in research and development